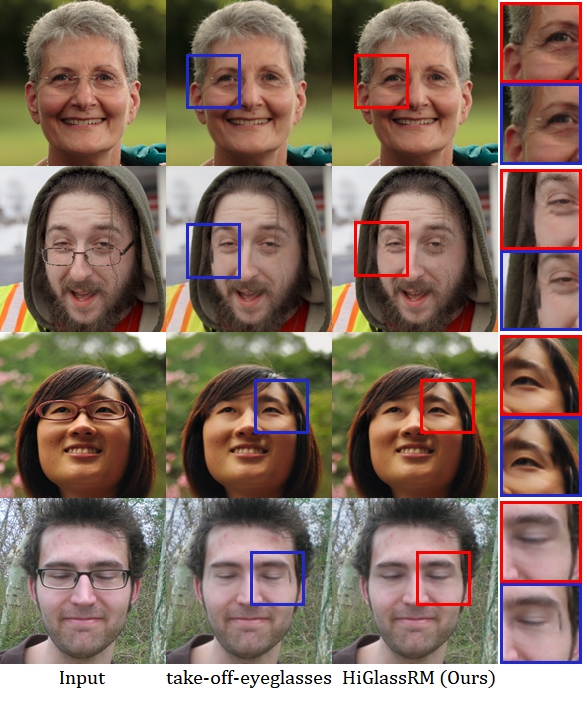
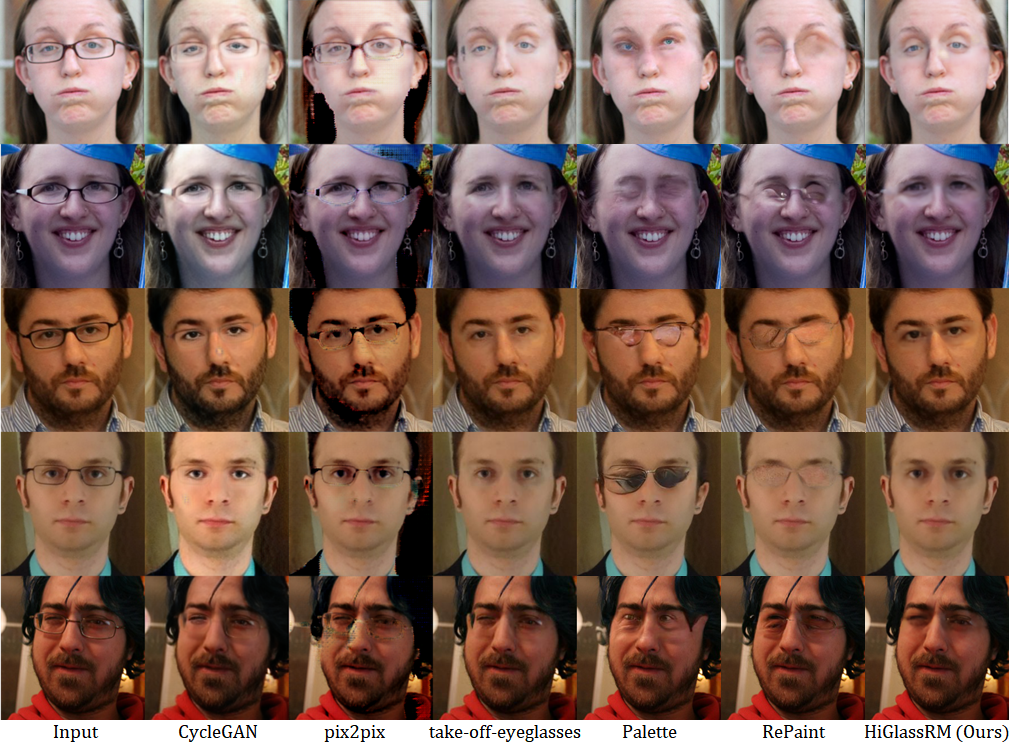
Figure1: Qualitative comparison on FFHQ [15]. Our HiGlassRM explicitly compensates this geometric distortion, preserving identity-consistent facial geometry and background alignment.overview
Abstract
HiGlass Dataset Overview
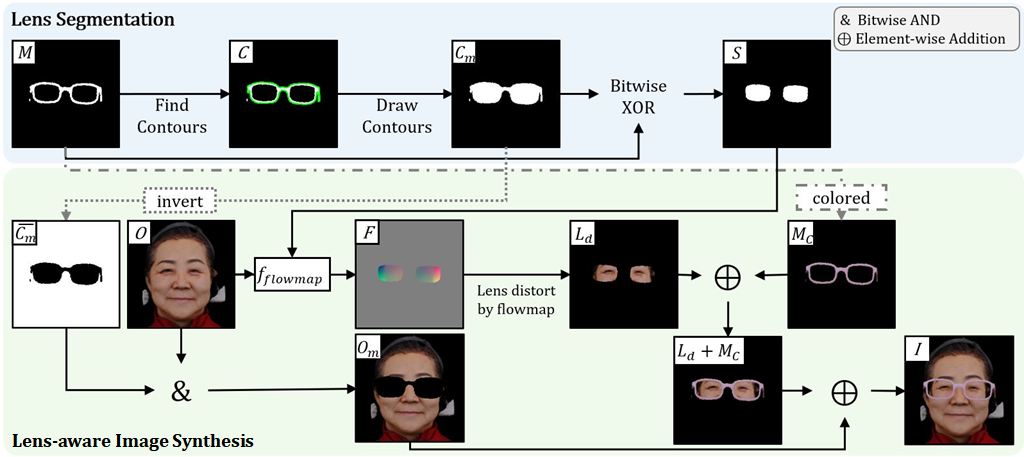 Figure3: HiGlass Dataset synthesis overview
Figure3: HiGlass Dataset synthesis overview
From the binary eyeglass-frame mask $M$, the outermost contour $C$ is detected and drawn to create the filled silhouette mask $C_m$. A bitwise XOR with $M$ yields the lens mask $S$. The complement $\overline{C}_m$ masks the face image $O$ to produce the background-preserved image $O_m$. A flow map $F$ is computed and applied inside $S$ to obtain the lens-distorted content $L_d$. Finally, the colored frame $M_C$ is added and the result is composited with $O_m$ to form the final image $I$.
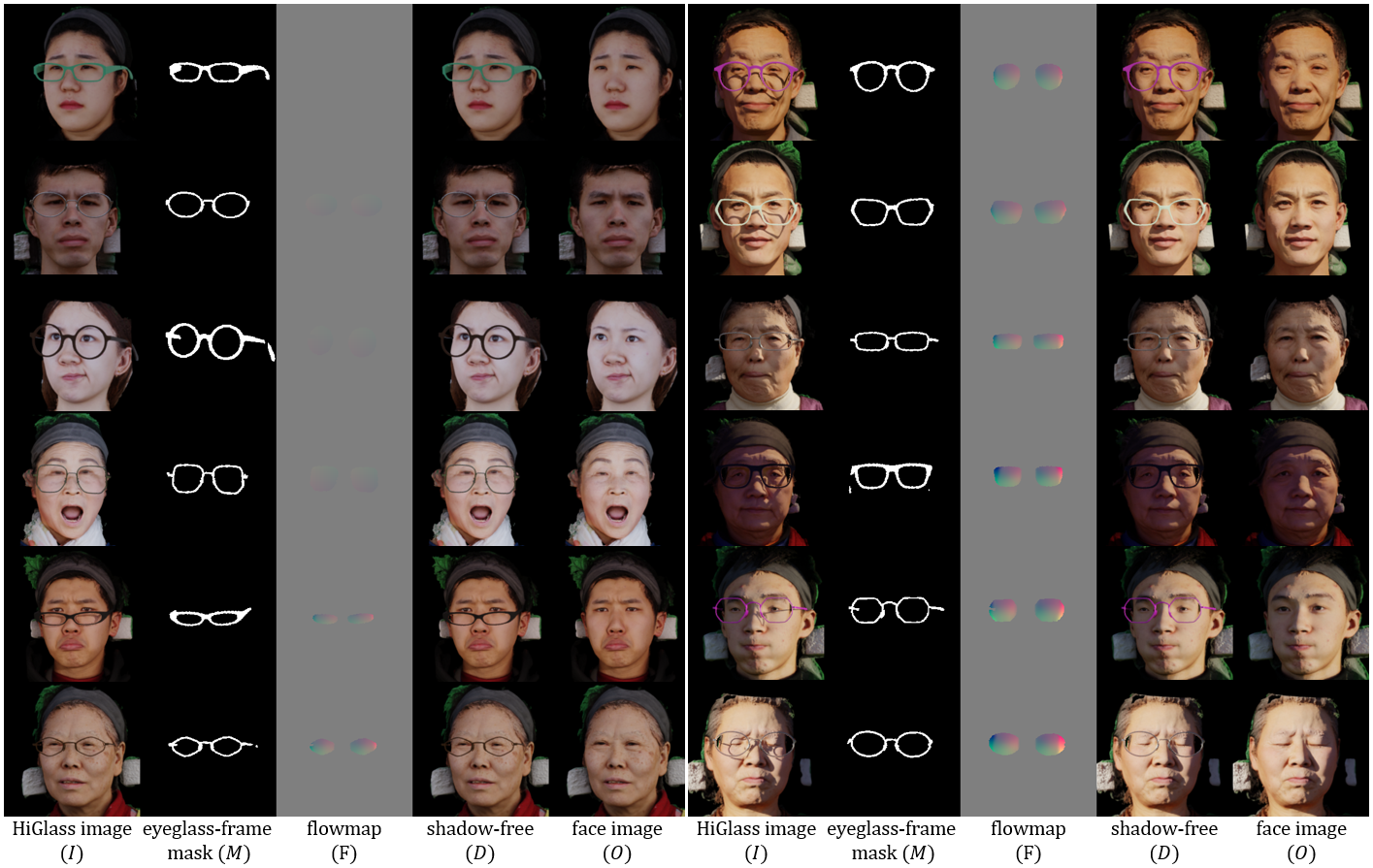 Figure6: Examples from HiGlass Dataset
Figure6: Examples from HiGlass Dataset
The HiGlass Dataset provides rich visual samples showcasing diversity in frame shapes and lens powers. Each paired sample contains five core components: $(I, M, F, D, O)$. The HiGlass image $I$ is the final composite with all synthesized optical effects. The binary eyeglass-frame mask $M$ localizes only the frames. The displacement flowmap $F$ encodes the geometric warp caused by the lens (e.g., minification or magnification). The shadow-free image $D$ is a rendered variant that retains these optical effects but removes cast shadows. Finally, the face image $O$ is the eyeglass-free supervision target.
HiGlassRM Overview
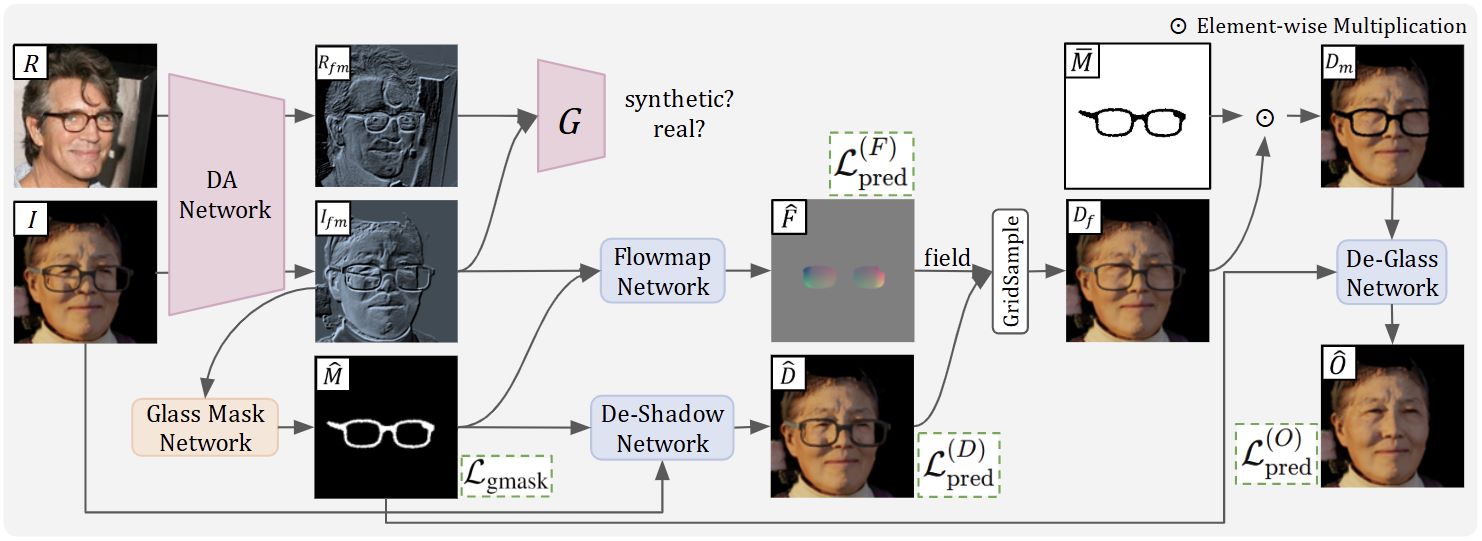 Figure4: Overview of the proposed HiGlassRM.
Figure4: Overview of the proposed HiGlassRM.
The framework begins by transforming the real image $R$ and synthetic image $I$ into unified feature maps $R_{fm}$ and $I_{fm}$ through the Domain Adaptation (DA) Network. The Glass Mask Network processes $I_{fm}$ to generate an eyeglass mask $\widehat{M}$, identifying the presence of eyeglasses. The De-Shadow Network takes $I$ and $\widehat{M}$ as input to produce a shadow-free image $\widehat{D}$. The Flowmap Network, using $I_{fm}$ and $\widehat{M}$, generates a flow map $\widehat{F}$ to correct distortion. This flow map is applied to $\widehat{D}$ through Grid Sampling, producing $D_f$. Next, element-wise multiplication with the inverted mask $\overline{M}$ yields the masked de-distorted image $D_m$. The De-Glass Network then processes $D_m$ and $\widehat{M}$ to generate the eyeglass-free image $\widehat{O}$.
Experimental Results on Real Data